RESEARCH
DIARY_

06
Brainwave Entrainment
Have you ever felt sad together while
comforting a friend who was crying? Or have you ever felt happy just
by watching a joyful puppy?
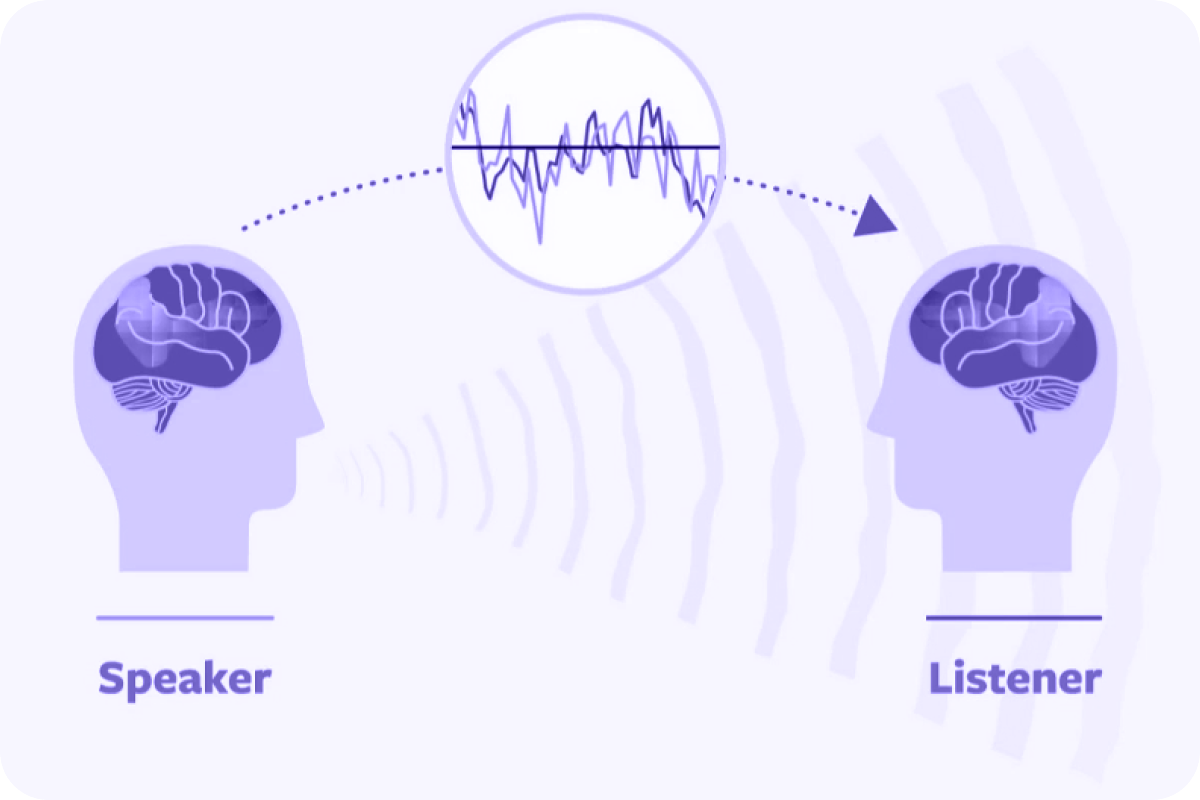
It turns out that our brains naturally sync with what we see and hear from the outside world. According to research by Princeton University professor Uri Hasson, when people share stories, their brain activity becomes aligned, helping them connect and understand each other better. Isn’t that amazing? Just by seeing or hearing something, the state of your brain can change!
It turns out that our brains naturally sync with what we see and hear from the outside world. According to research by Princeton University professor Uri Hasson, when people share stories, their brain activity becomes aligned, helping them connect and understand each other better. Isn’t that amazing? Just by seeing or hearing something, the state of your brain can change!
This also applies to brainwaves. When you listen to alpha wave
frequencies, your brain adjusts to those alpha waves. If you listen to
theta waves, your brain synchronizes with them, and this is called
brainwave entrainment. Brainwave Entrainment, also known as brainwave
synchronization, is a method of arousing the brain to enter a specific
state using different factors, such as sound, light, and
electromagnetic fields. The pulses created by the factor evoke the
brain’s frequency, which results in the brainwave aligning with the
frequency of the beat of the factor. Brainwave entrainment can
influence your mood, mental state, and even physical condition. Many
studies have proven that using external stimuli, like sound or light,
can have real effects on your brain.

One example is sleep. When you’re in deep sleep, your brain mostly
produces delta waves. If someone listens to delta wave frequencies even
though they’re awake, the brain tries to sync with those delta waves and
leads the body into a deep sleep state. But here’s the tricky part:
delta waves are around 0.5-4Hz, while humans can only hear frequencies
starting from 20Hz. Then how do we make people hear delta waves? That’s
a really tough challenge. I had to read tons of difficult research
papers to figure this out. So I’ll save that story for the next article!